Abstract
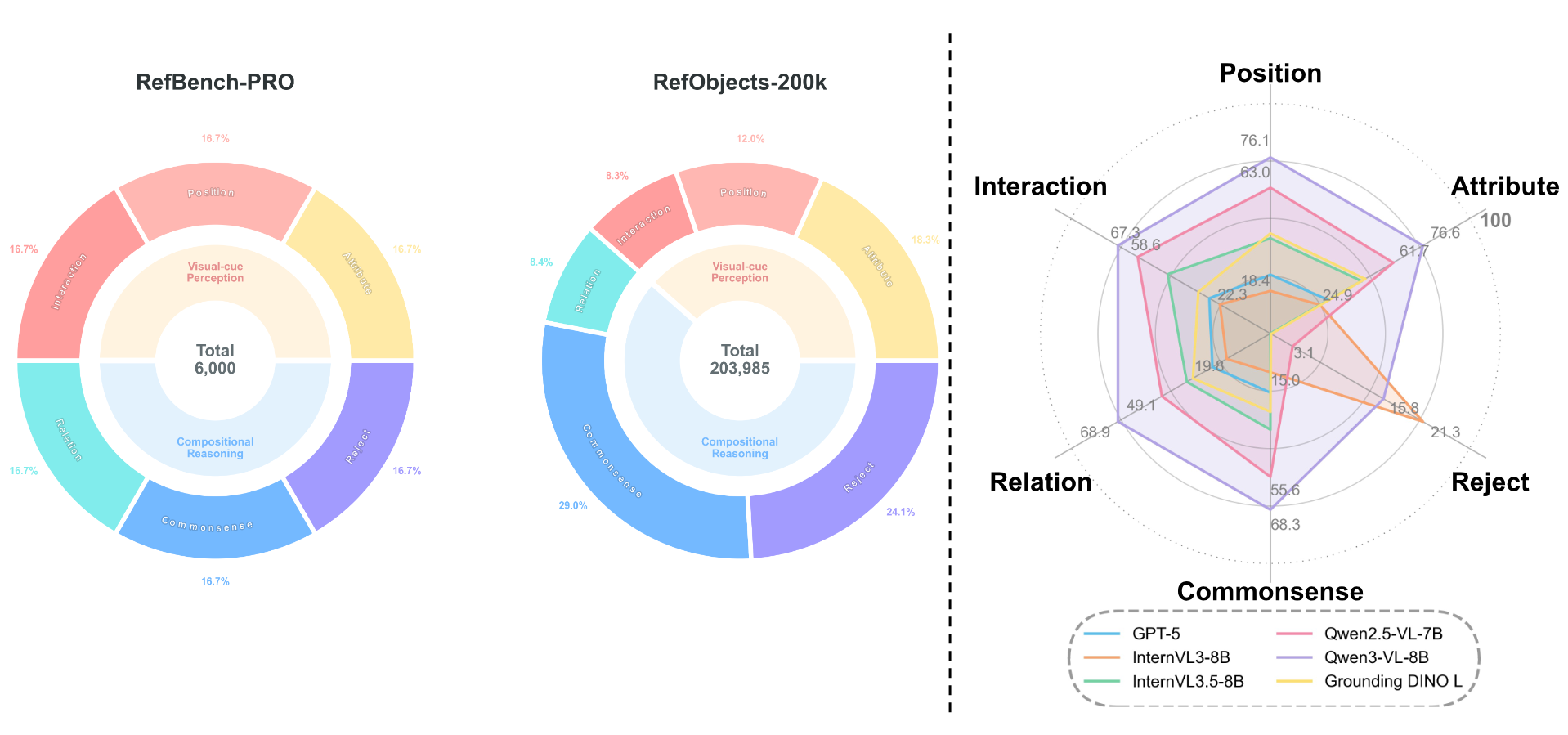
Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) is a vision-language task that localizes a specific image region based on a textual description. Existing REC benchmarks primarily evaluate perceptual capabilities and lack interpretable scoring mechanisms, which cannot reveal the grounding capability of Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM) across different cognitive abilities. To address this limitation, we introduce RefBench-PRO, a comprehensive REC benchmark, which decomposes referring expressions into two core dimensions, i.e., perception and reasoning, and further subdivides them into six progressively challenging tasks, such as attribute, position, interaction, commonsense, relation and reject. We also develop a fully automated data-generation pipeline that produces diverse referring expressions across these six sub-dimensions. Furthermore, We propose Ref-R1, an RL-based learning scheme, which incorporates Dynamic IoU-based GRPO to improve localization accuracy under increasingly complex reasoning conditions, establishing a stronger baseline for REC. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our RefBench-PRO enables interpretable evaluation of MLLM on referring expression comprehension, presenting greater challenges in both perception and reasoning.
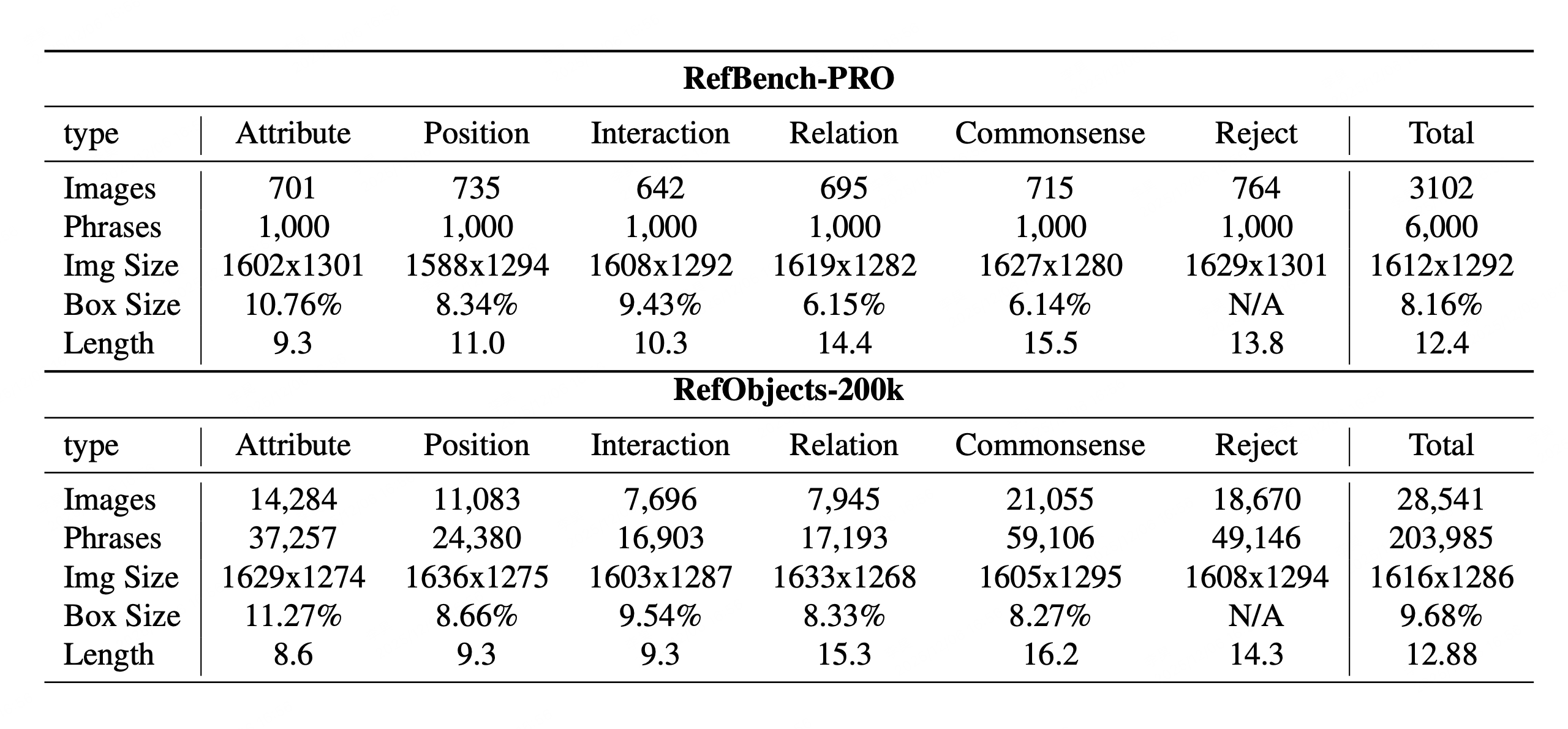
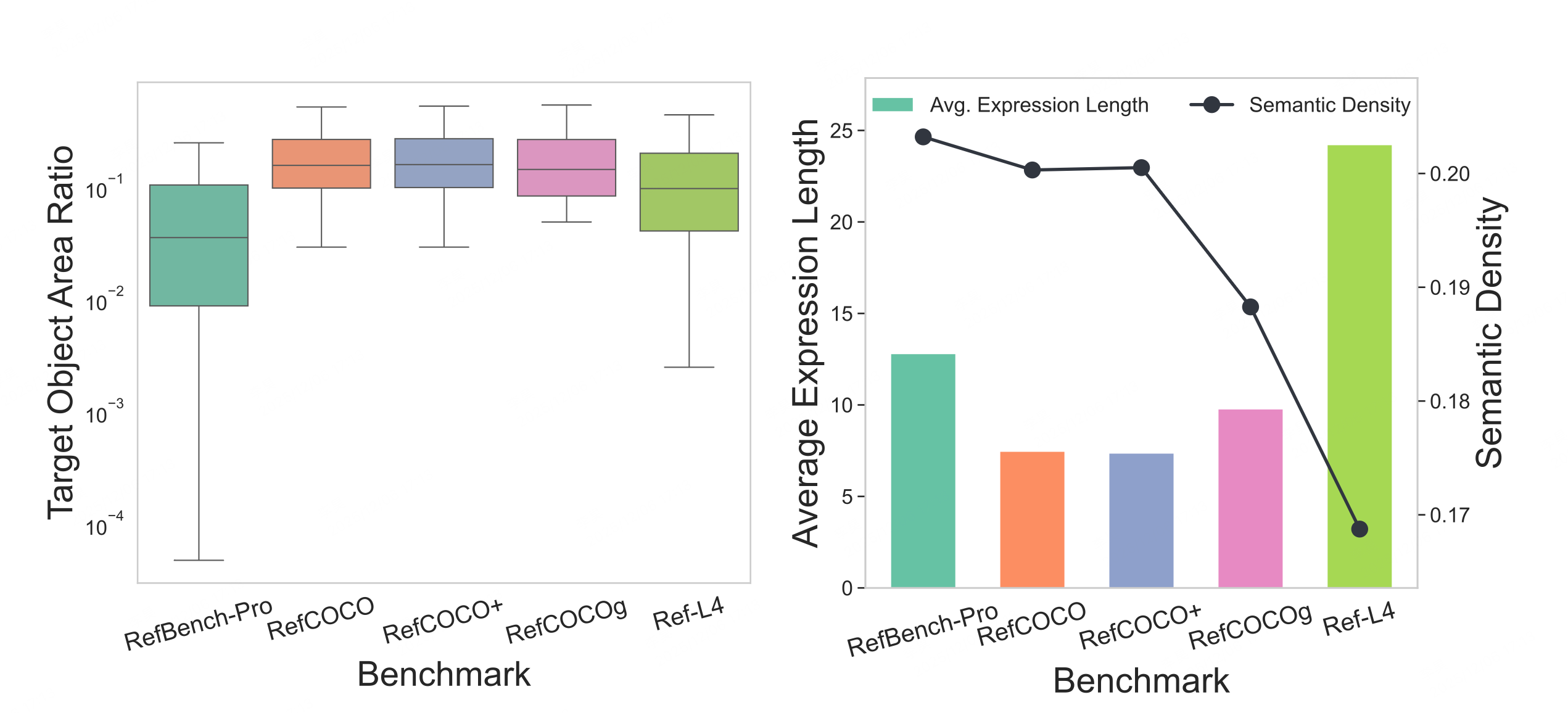
Benchmark Statistic
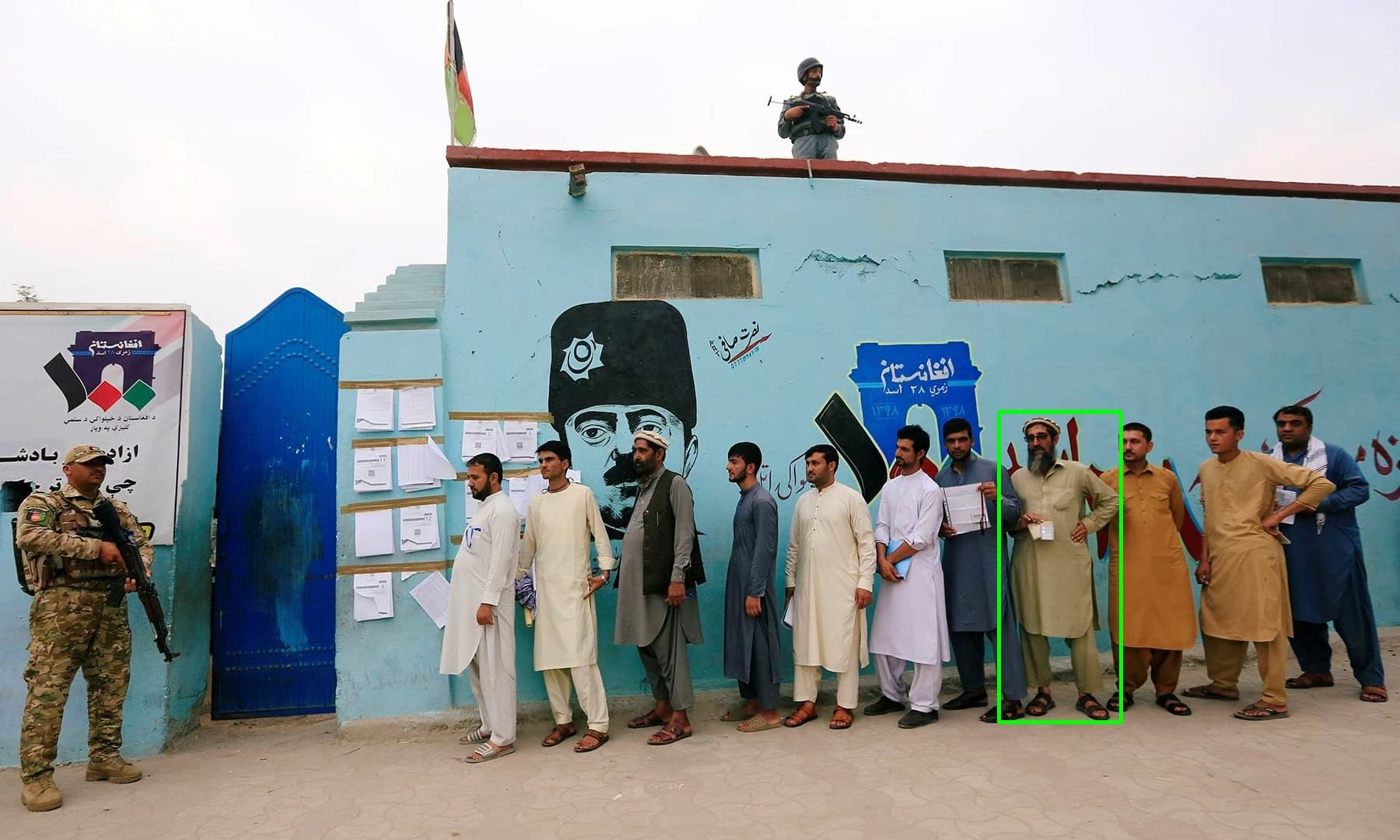
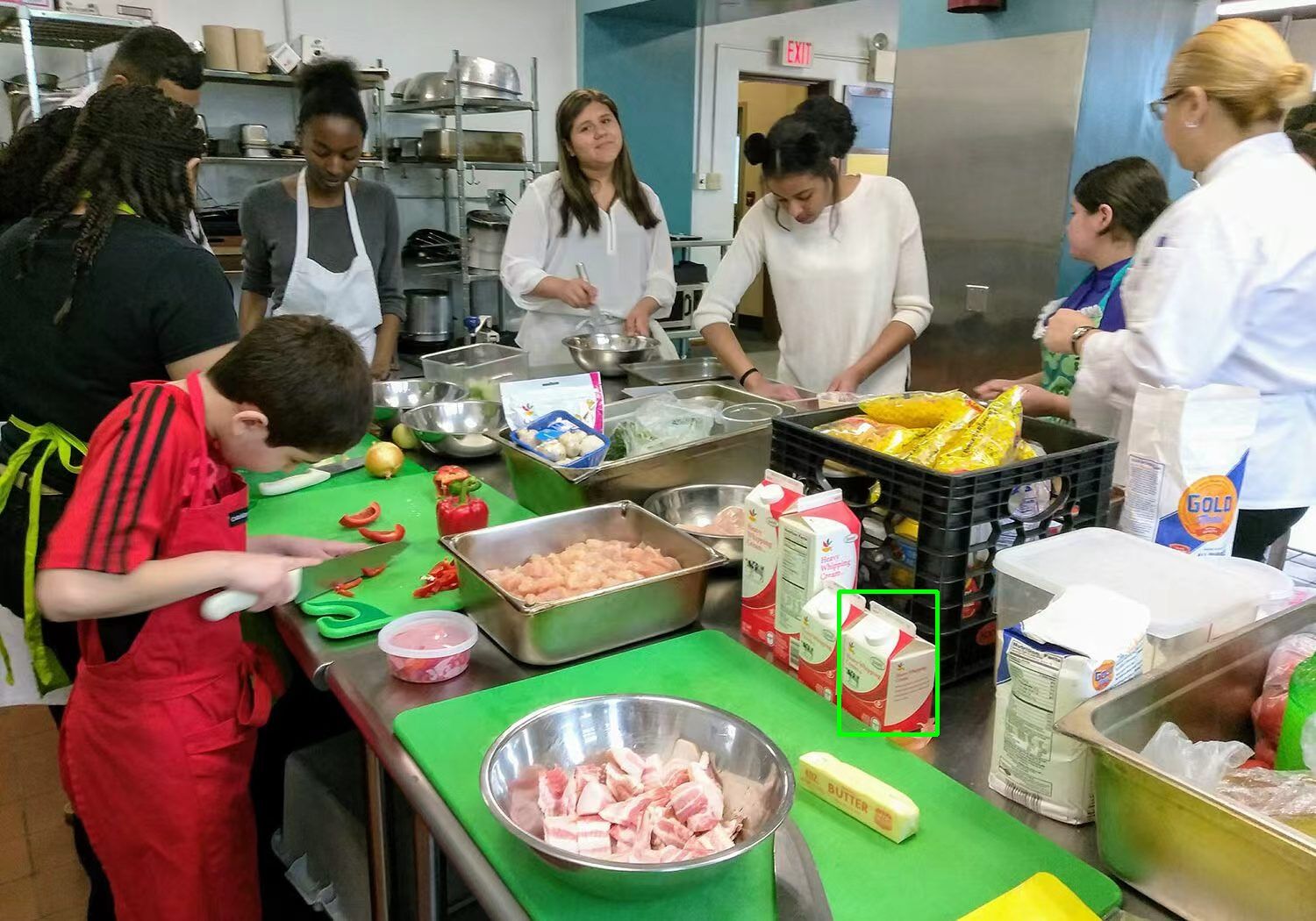
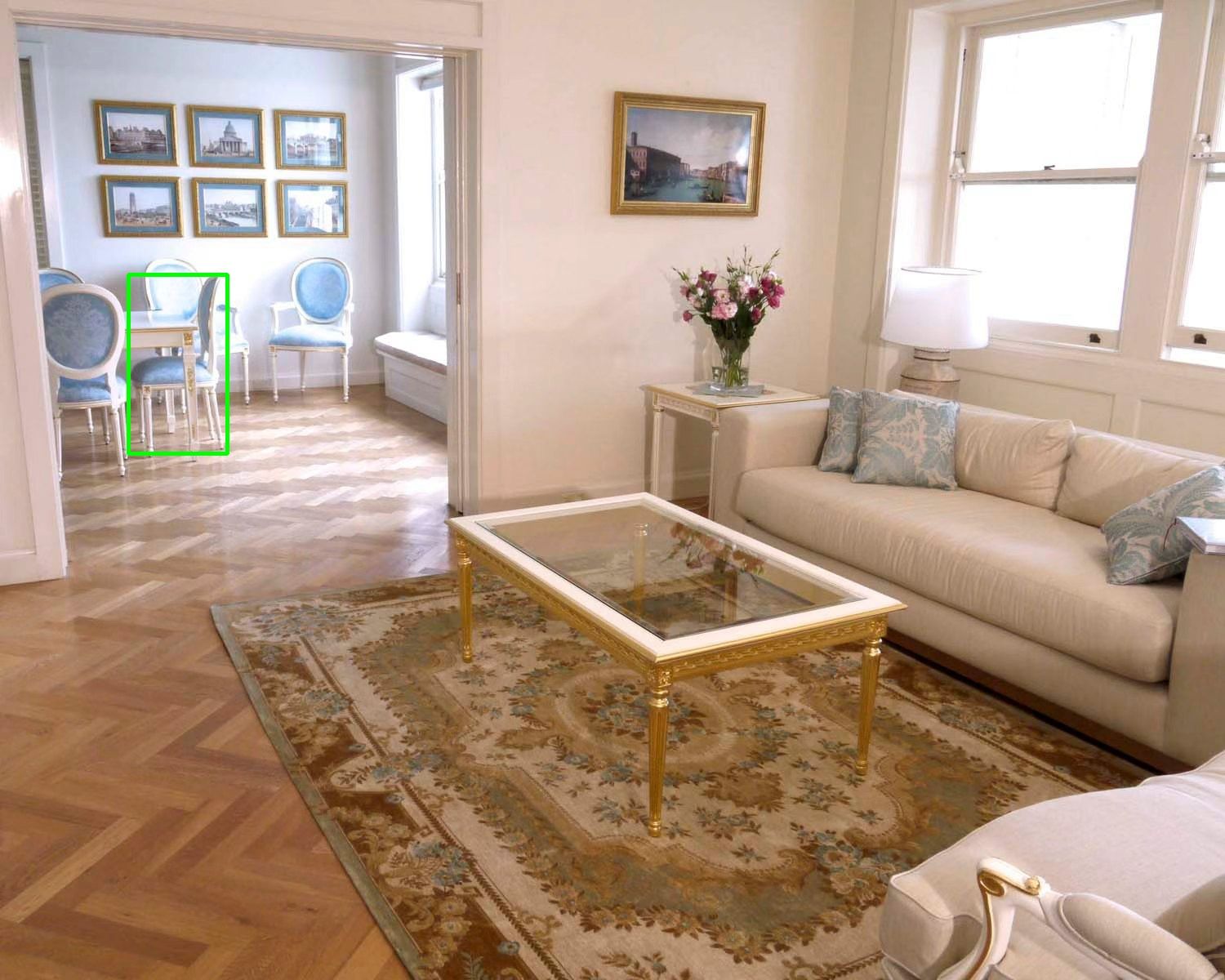
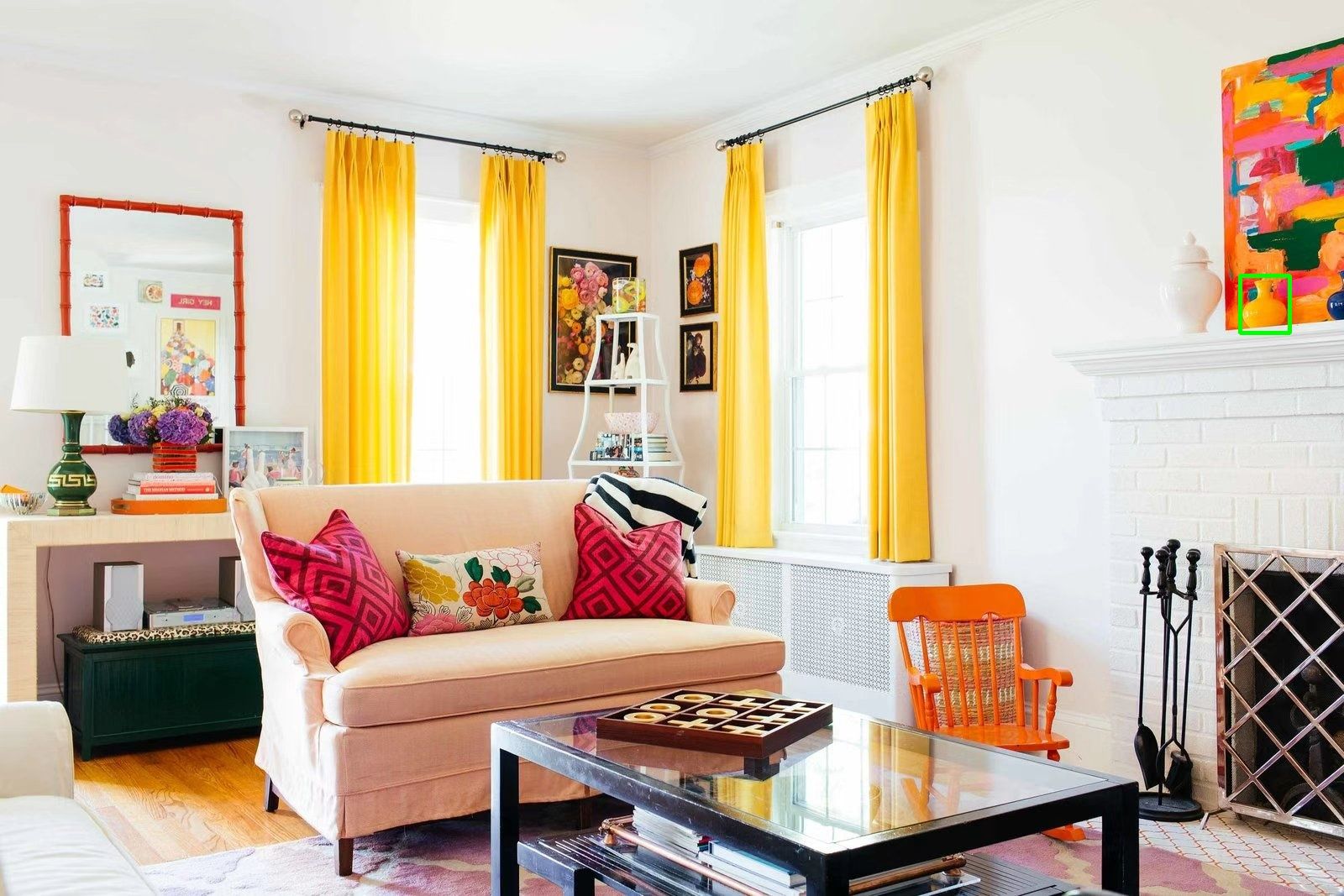
Benchmark Example
Leaderboard
Overall | Visual-cue Perception | Compositional Reasoning | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLEE | 2023-12 | 36.1 | 31.2 | 48.2 | 38.4 | 34.5 | 40.4 | 31.4 | 27.9 | 7.1 | 29.7 |
| Grounding DINO L | 2023-03 | 37.6 | 31.3 | 47.5 | 43.3 | 31.8 | 40.9 | 35.0 | 30.3 | 0.1 | 32.7 |
| Gemini-2.5-pro | 2025-03 | 9.6 | 8.0 | 10.4 | 11.5 | 10.8 | 10.9 | 7.2 | 8.2 | - | 7.7 |
| GPT-4o | 2024-05 | 12.1 | 10.1 | 11.7 | 12.8 | 11.9 | 12.1 | 12.4 | 11.6 | - | 12.0 |
| GPT-5 | 2025-08 | 26.1 | 21.8 | 29.2 | 25.5 | 27.0 | 27.2 | 26.2 | 22.9 | - | 24.6 |
| PaDT-3B | 2025-10 | 26.6 | 22.2 | 30.4 | 28.0 | 30.4 | 29.6 | 23.7 | 20.8 | - | 22.3 |
| VLM-R1-3B | 2025-04 | 54.4 | 45.3 | 59.0 | 58.0 | 54.1 | 57.0 | 47.8 | 53.2 | - | 50.5 |
| ChatRex-7B | 2024-11 | 49.5 | 41.3 | 54.7 | 51.1 | 53.2 | 53.0 | 45.1 | 43.4 | - | 44.2 |
| Migician-7B | 2025-01 | 52.3 | 43.6 | 57.3 | 59.7 | 52.8 | 56.6 | 45.4 | 46.1 | - | 45.7 |
| UniVG-R1-7B | 2025-05 | 53.0 | 44.2 | 59.4 | 57.2 | 55.1 | 57.2 | 48.3 | 44.9 | - | 46.6 |
| Rex-Thinker-7B | 2025-06 | 63.6 | 53.0 | 67.1 | 64.5 | 61.7 | 64.4 | 59.3 | 65.6 | - | 62.4 |
| CogVLM-Grounding-17B | 2023-11 | 57.1 | 47.5 | 62.4 | 62.4 | 55.9 | 60.2 | 49.4 | 55.2 | - | 52.3 |
| Qwen2-VL-7B | 2024-09 | 45.4 | 42.6 | 55.3 | 47.8 | 37.8 | 47.0 | 39.4 | 46.5 | 28.5 | 43.0 |
| Mimo-VL-RL-7B | 2025-06 | 56.3 | 46.9 | 60.9 | 58.4 | 57.3 | 58.9 | 51.8 | 52.9 | 0.1 | 52.4 |
| Qwen2.5-VL-7B | 2025-02 | 57.6 | 48.5 | 61.7 | 63.0 | 58.6 | 61.1 | 49.1 | 55.6 | 3.1 | 52.3 |
| InternVL3-8B | 2025-04 | 20.1 | 20.3 | 24.9 | 18.4 | 22.3 | 21.9 | 19.8 | 15.0 | 21.3 | 17.4 |
| InternVL3.5-8B | 2025-08 | 41.5 | 34.6 | 45.7 | 41.2 | 45.3 | 44.1 | 37.8 | 37.3 | - | 37.5 |
| LLaVA-OneVision-1.5-8B | 2025-09 | 50.7 | 42.3 | 54.5 | 54.0 | 48.4 | 52.3 | 48.1 | 48.6 | - | 48.3 |
| Qwen3-VL-8B | 2025-10 | 71.4 | 62.2 | 76.6 | 76.1 | 67.3 | 73.3 | 68.9 | 68.3 | 15.8 | 68.6 |
| Ovis2.5-9B | 2025-08 | 61.7 | 51.5 | 65.7 | 63.6 | 59.7 | 63.0 | 58.7 | 61.0 | - | 59.9 |
| GLM-4.1V-Base-9B | 2025-07 | 60.1 | 50.1 | 62.9 | 61.0 | 57.7 | 60.5 | 57.0 | 61.9 | - | 59.4 |
| LLaVA-OneVision-72B | 2024-08 | 56.5 | 47.1 | 60.1 | 59.4 | 53.7 | 57.7 | 54.2 | 55.0 | - | 54.6 |
| Qwen2.5-VL-72B | 2025-02 | 66.7 | 59.5 | 68.6 | 69.1 | 69.4 | 69.1 | 61.6 | 64.8 | 23.6 | 63.2 |
| InternVL3-78B | 2025-04 | 21.8 | 22.3 | 35.0 | 24.9 | 28.2 | 29.4 | 24.3 | 20.8 | 24.8 | 22.5 |
| Qwen3-VL-32B | 2025-10 | 79.0 | 66.6 | 82.7 | 80.3 | 76.3 | 79.8 | 74.1 | 81.6 | 4.5 | 77.9 |
BibTeX citation
@article{gao2025refbench, title={RefBench-PRO: Perceptual and Reasoning Oriented Benchmark for Referring Expression Comprehension}, author={Gao, Tianyi and Li, Hao and Fang, Han and Wei, Xin and Dong, Xiaodong and Sun, Hongbo and Yuan, Ye and He, Zhongjiang and Xu, Jinglin and Xin, Jingmin and others}, journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.06276}, year={2025}}










